With the growth of electric vehicles (EVs) as a viable transportation option, it is no surprise that this new movement has become integrated into the larger energy infrastructure.
As EVs are parked roughly 95% of their time and have large batteries, they offer an opportunity to keep the lights on during outages and support utilities during periods of high demand. This opportunity is called bidirectional or vehicle-to-grid (V2G) charging.
Bidirectional EV charging is exactly what it sounds like: EV charging that goes two ways. And, it has been deemed “one of the legitimate game changers” by Clifford Rechtschaffen, commissioner of the California Public Utilities Commission.
Let’s take a look at how V2G works, who benefits from its use, and what this means for EV owners in the future.
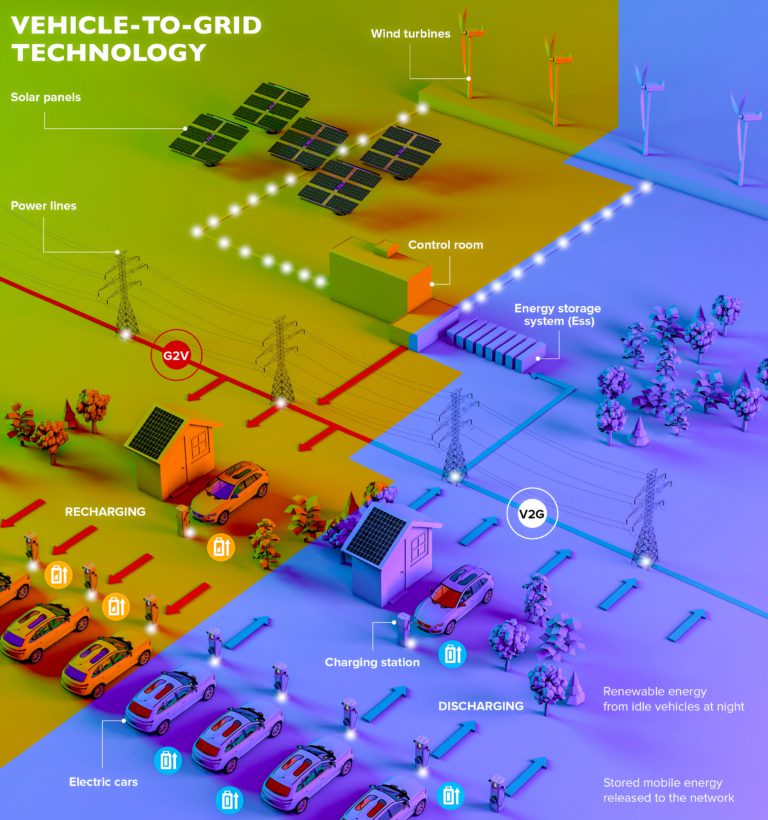
How V2G Works
The concept behind V2G is relatively simple—it allows EV owners to charge their vehicles while providing extra electricity to the grid when needed. This is done through a charger (check out the different types of EV chargers here) that connects to both your car’s battery and your home’s electrical system.
But how does it work?
When an EV is charged AC electricity is converted using your car’s own converter or a converter located within your charger to DC electricity that can then be used by your car.
Want to hear the best part?
When you have excess energy stored you can even make money by selling that excess energy back to the grid or back to your utility company!
For example, if there is a sudden spike in demand due to everyone turning their AC on during a heat wave, utilities can pay homeowners for their battery power. In return for supplying extra electricity to the grid, EV owners will get paid based on market rates for electricity or other incentives like credits towards future bills or payments from third-party energy providers.
As a matter of fact, in Colorado, the state has mandated that utilities install EV chargers in certain areas and offer EV owners discounts on their electricity bills, making V2G a win-win situation for all involved.
Who Benefits From V2G?
One benefit that comes with V2G is that it creates an additional revenue stream for EV owners as they get paid for supplying extra electricity to the grid. Beyond this economic incentive, V2G also helps reduce stress on existing energy resources such as natural gas plants which are often used when energy demands increase suddenly.
Additionally, it helps promote renewable sources such as solar and wind power since these energies are most readily available when there is low demand from consumers or businesses–times when EV batteries can help pick up some of the slack by returning power back into the grid.
Vehicle-to-grid charging (V2G) offers many advantages both economically and environmentally; however, more work needs to be done before this technology can reach its full potential on a large scale basis.
A concerted effort between government agencies, automakers, utility companies, and EV owners across different markets must work together in order to make this game-changing technology a reality by utilizing existing resources in smarter ways while promoting renewable sources of energy production at lower costs than traditional methods.
With these combined efforts we can bring about the much-needed change in our current energy infrastructure as well as create new incentives for EV owners everywhere!
Curious to Learn More About The Benefits of Switching to EV?
Check out our Guide on EV Charging Stations in Colorado
As of July 2019, there were a total of 3,764 public electric vehicle (EV) charging stations in Colorado. With the EV market expanding several consumers are making the switch to electric but one major consideration is installing EV charging stations. This guide aims to share all the information consumers will need to know before investing in an EV charging station for their home or business.

